BOTOX is a highly popular cosmetic treatment, a neurotoxin that smoothes lines and wrinkles. It works by blocking muscle movements in specific areas of the face.
BOTOX also can help with certain medical conditions, such as neck muscle spasms and excessive sweating. It is important to have your BOTOX injections done by a trained professional. Contact House of Aesthetix now!
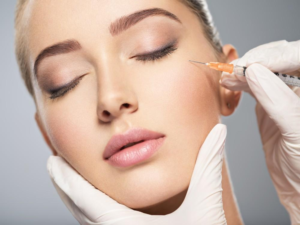
When most people hear the word Botox, they think of celebrities with too-tight faces or those called out in tabloids for having “work done.” But what many don’t know is that the cosmetic use of this drug wasn’t its original purpose. Botox is an injectable that blocks certain nerve signals, which causes muscles to relax. This reduces or eliminates fine lines and wrinkles. The drug is injected into specific facial muscles in a short, simple procedure that takes less than 30 minutes and can be performed in a doctor’s office. The drug is a purified form of botulinum toxin type A, and although different brands may use slightly different versions of the neuromodulator, they all work the same way to smooth wrinkles.
In addition to smoothing out fine lines, the drug also is used to treat some medical conditions. For example, it is injected to help control overactive bladders in adults with neurologic conditions such as spinal cord injury or multiple sclerosis. It also is used to treat a condition that causes the muscles of the neck to twist and rotate uncontrollably, a disorder known as cervical dystonia. It is also used to treat muscle stiffness of the arms, legs, hands, and feet in patients 2 years of age or older, a condition called spasticity.
Before a person receives BOTOX, the doctor rubs an anesthetic cream on the area to be treated. Then the health care professional uses a small needle to inject the medication into the affected muscle. The injections only take a few seconds and are painless. People often return to their normal activities right after the treatment.
Botox can cause serious problems if it is injected into the wrong areas or by an inexperienced healthcare professional. It is important to only use this medicine with a trained, licensed healthcare professional. You should not try to get Botox injections from more than one health care provider at a time, and you should not receive the injectable drug from anyone who is not a licensed healthcare professional. If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, you should not receive the drug.
How is Botox injected?
Botox is injected into the muscles of the face using fine needles. Your practitioner will cleanse the treatment area and apply a topical anesthetic cream to prevent discomfort. Botox is diluted with a special saline solution before use, which allows a smaller amount to be injected at each site. This minimizes the number of times your facial muscles will contract and relax, reducing the appearance of wrinkles.
When injected, the toxin blocks nerve impulses at the junction where muscle cells connect to nerve endings. This prevents the release of a chemical messenger called acetylcholine, which causes the muscle cells to contract or shorten. Over time, the muscle cells lose their ability to contract and the wrinkles soften and fade away.
The injection procedure takes just minutes, and you can return to normal activities immediately afterward. Some patients experience redness, swelling or bruising at the injection site, but these effects typically subside within a few hours.
Although BOTOX is most often injected for cosmetic purposes, it has many medical applications. Besides smoothing out wrinkles, it is also used to treat migraine headaches, neck pain and TMJ (temporomandibular joint disorder) by weakening the muscles that cause them.
The toxin used in BOTOX is made by a bacterium called Clostridium botulinum. The specific type of toxin that is used for medical purposes has been purified and stabilized in a lab for maximum safety. This toxin cannot be ingested in large quantities because it can cause a dangerous nervous system disease called botulism, which affects breathing.
Botox is very safe and does not have serious side effects when injected by an experienced physician. Rarely, some patients may have blurred or double vision and may develop drooping eyelids if the medication is injected into certain muscles around the eyes. If you have these symptoms, tell your doctor right away.
A few months after BOTOX injection, the nerve terminals in the muscles begin to regenerate and regain their normal function. Injections are repeated periodically to maintain the effect.
What are the benefits of Botox?
BOTOX is FDA-approved for banishing fine lines and wrinkles. However, the versatile injectable can also help with a number of medical conditions such as chronic migraines and excessive sweating. It’s even becoming popular for enhancing facial symmetry and slimming the jawline.
Botox, Dysport, and Xeomin are all derived from a purified form of botulinum toxin type A, so there is no risk of botulism when used correctly. The injections work by blocking the nerve impulses that contract muscles, softening their appearance and helping prevent them from tightening. The results of these wrinkle-smoothing treatments typically last about 3 to 6 months.
While the cosmetic benefits of Botox are well-known, many people are unaware that this injectable can also be used to treat certain medical conditions. One example is Bell’s Palsy, a health condition that causes the muscles of the face to weaken or completely paralyze. When treated with Botox, the muscle on the affected side relaxes, and the unaffected side becomes stronger, restoring facial symmetry.
Another common use of the injectable is to reduce urinary incontinence. The neurotoxin works by blocking the nerve signals that cause the bladder to contract. As a result, it prevents the bladder from filling and emptying.
Botox is also widely used for reducing neck pain, back pain, and headaches. When injected into the temples or forehead, the drug stops the muscles from tightening and relieves tension. It can also be used to reduce sweating in those with hyperhidrosis, a condition that causes excessive sweating.
If you’re considering Botox, it’s important to only use a licensed and experienced healthcare professional. Working with someone who is not licensed may save you money, but it can also increase the risk of complications. It’s also best to avoid Botox if you’re pregnant or breastfeeding.
The injection process is relatively quick and painless, especially if your provider uses pre-icing or other strategies to minimize discomfort. The needle is also very small, so you shouldn’t feel much of anything beyond a slight prick. In addition, most providers offer numbing creams or other forms of anesthesia if you’re concerned about pain.
What are the risks of Botox?
While Botox is viewed by many as safe and effective, it’s not without its risks. Most adverse reactions are minor and temporary. They can include pain and bruising at the injection site.
When injected by an experienced professional, Botox can be used to treat the fine lines and wrinkles that form in the face over time. It can also help to relax overactive muscles, which can lead to facial spasms. In fact, Botox has been used to treat patients with neck spasms related to Cerebral Palsy and crossed eyes (esotropia). Injections can relax the muscle and reduce the severity of the symptoms.
Those interested in getting Botox injections to address signs of aging should find an experienced, board-certified plastic surgeon. They can apply a topical numbing agent to the skin before the procedure to ensure comfort. The actual injections only take a few minutes. Some people may experience a mild headache after the injections, but this usually subsides within 24 hours.
One of the most serious risks of Botox is an allergic reaction to the substance. This can happen if the solution is improperly stored or prepared. It’s also possible to develop antibodies to the neurotoxin, which can affect the effectiveness of future treatments.
It’s important to discuss potential side effects and risks with your doctor before undergoing any treatment. They can assess your unique health situation and aesthetic goals to determine if this is the best option for you.
Some of the more common side effects associated with Botox include a headache, flu-like symptoms and a temporary weakness or drooping in the area treated. A more severe side effect is an infection, which can occur when the needle breaks the skin or enters a muscle. This can lead to a local bacterial infection and should be treated as soon as possible.
Other less common complications can include bruising at the injection site, which is called ecchymosis. This happens when the needle injures a blood vessel, most commonly in or around the eye area. Medications like anticoagulants and blood thinners can increase the risk of this complication, so you should avoid them for several days before your appointment. It’s also a good idea to avoid alcohol and NSAIDs before your treatment, as these can make you more prone to bruising.